
Oplead Lead Management : Streamline Your Sales Pipeline with Lead Management Excellence
Oplead Lead Management: in summary
Oplead Lead Management is designed to enhance your sales by efficiently managing and nurturing leads. Ideal for sales teams and SMEs, this solution offers intuitive lead scoring, seamless integrations, and advanced reporting capabilities to keep you ahead of the competition.
What are the main features of Oplead Lead Management?
Efficient Lead Scoring
Oplead's lead scoring mechanism helps prioritize leads based on their likelihood to convert, ensuring you focus on the most promising opportunities.
- Automatic lead scoring based on engagement metrics
- Customizable scoring criteria to fit your business needs
- Real-time updates to keep lead statuses accurate
Seamless CRM Integrations
Oplead integrates effortlessly with your existing CRM systems, providing a unified and consistent approach to lead management.
- One-click synchronization with popular CRMs like Salesforce and HubSpot
- Data import/export features for flexibility
- Elimination of data silos
Advanced Reporting Capabilities
Track important metrics and gain actionable insights with Oplead's advanced reporting features, which are designed to optimize performance.
- Real-time dashboards displaying key sales metrics
- Customizable reports tailored to your business context
- In-depth analyses to identify trends and improvement areas
Automated Lead Nurturing
Automate repetitive tasks and nurture leads through personalized workflows, improving conversion rates and saving time.
- Drip email campaigns
- Task and appointment scheduling
- Behavior-triggered follow-ups
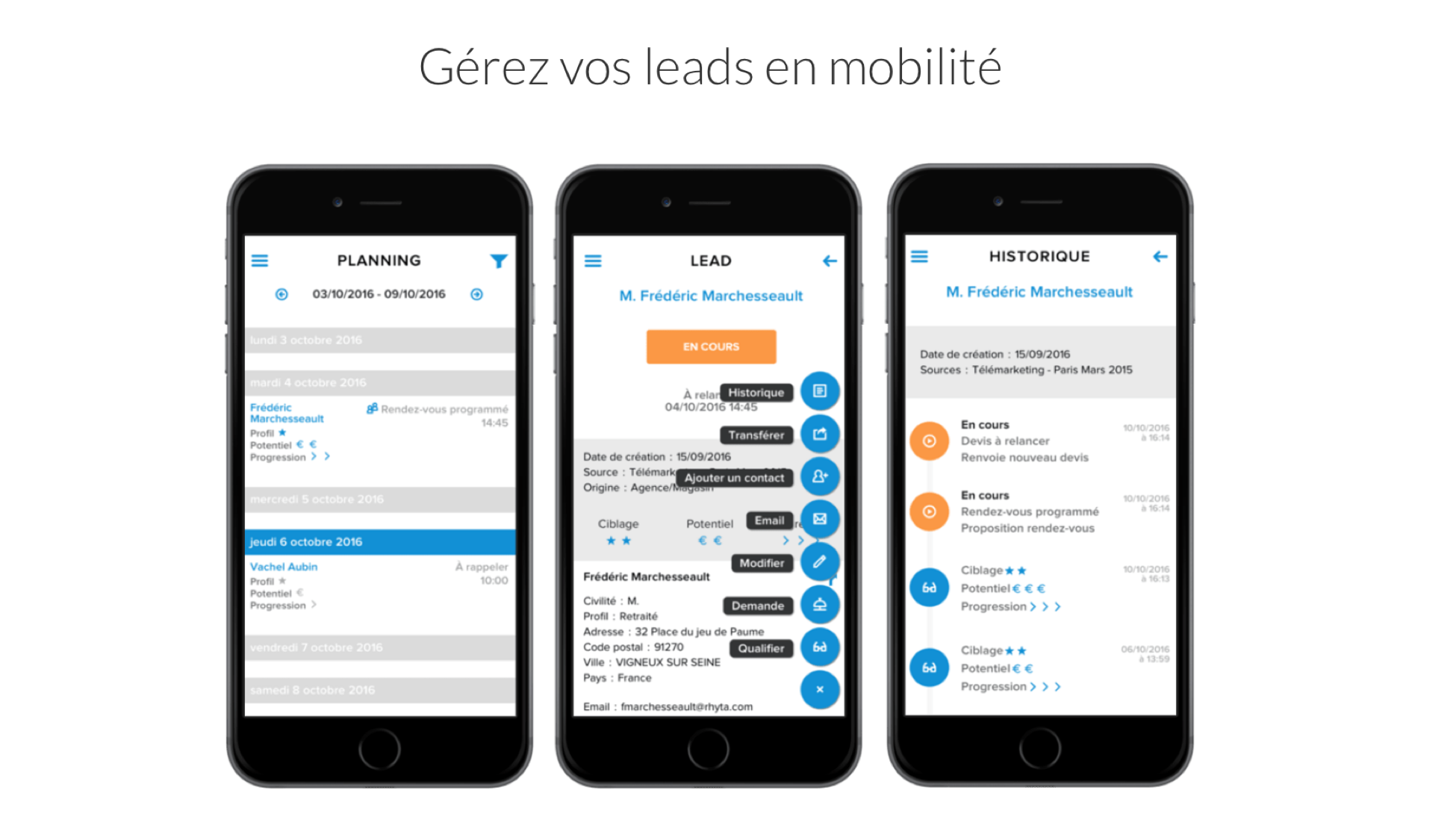 Oplead Lead Management - Oplead Lead Management on Mobile
Oplead Lead Management - Oplead Lead Management on Mobile 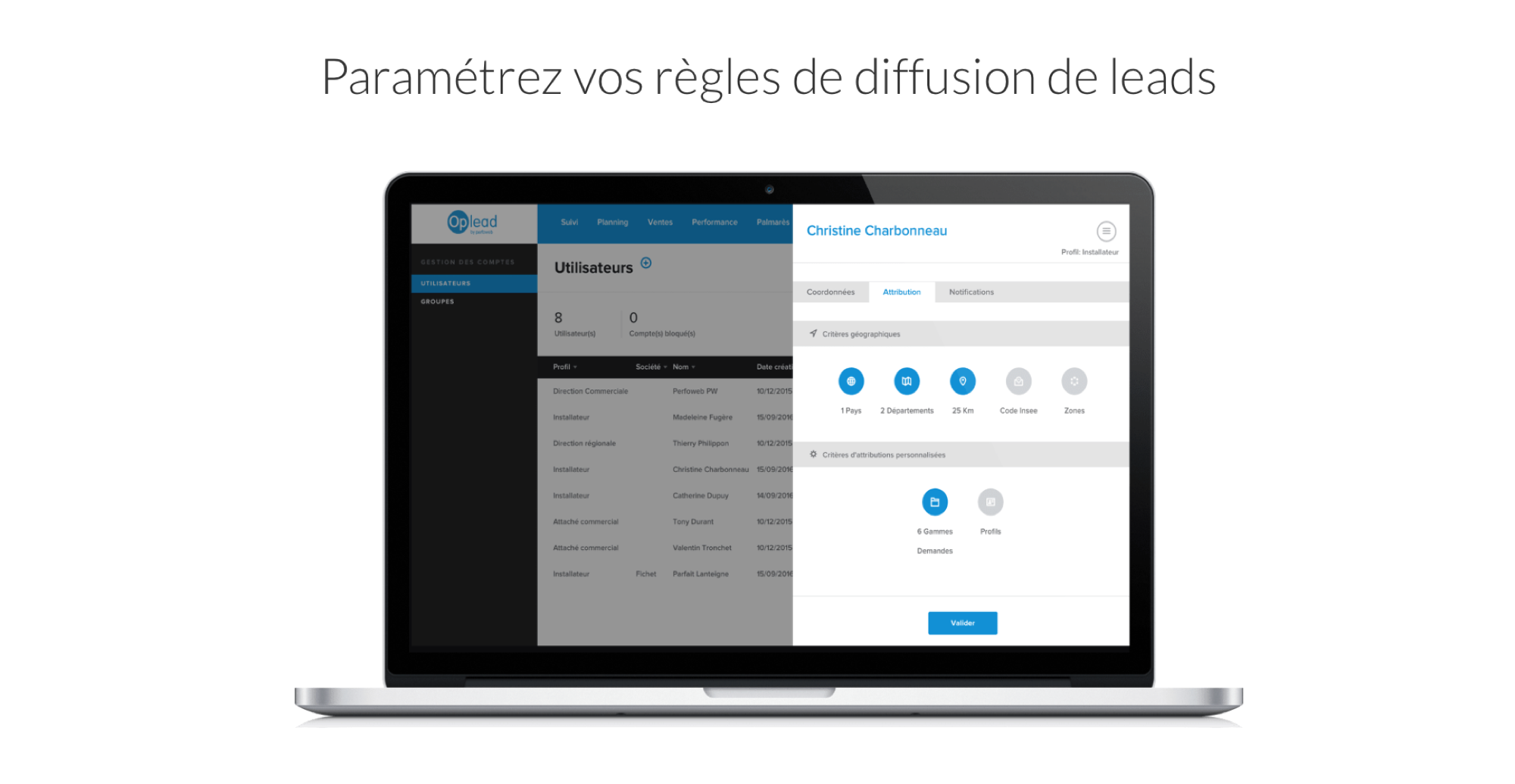 Oplead Lead Management - Lead distribution setup
Oplead Lead Management - Lead distribution setup 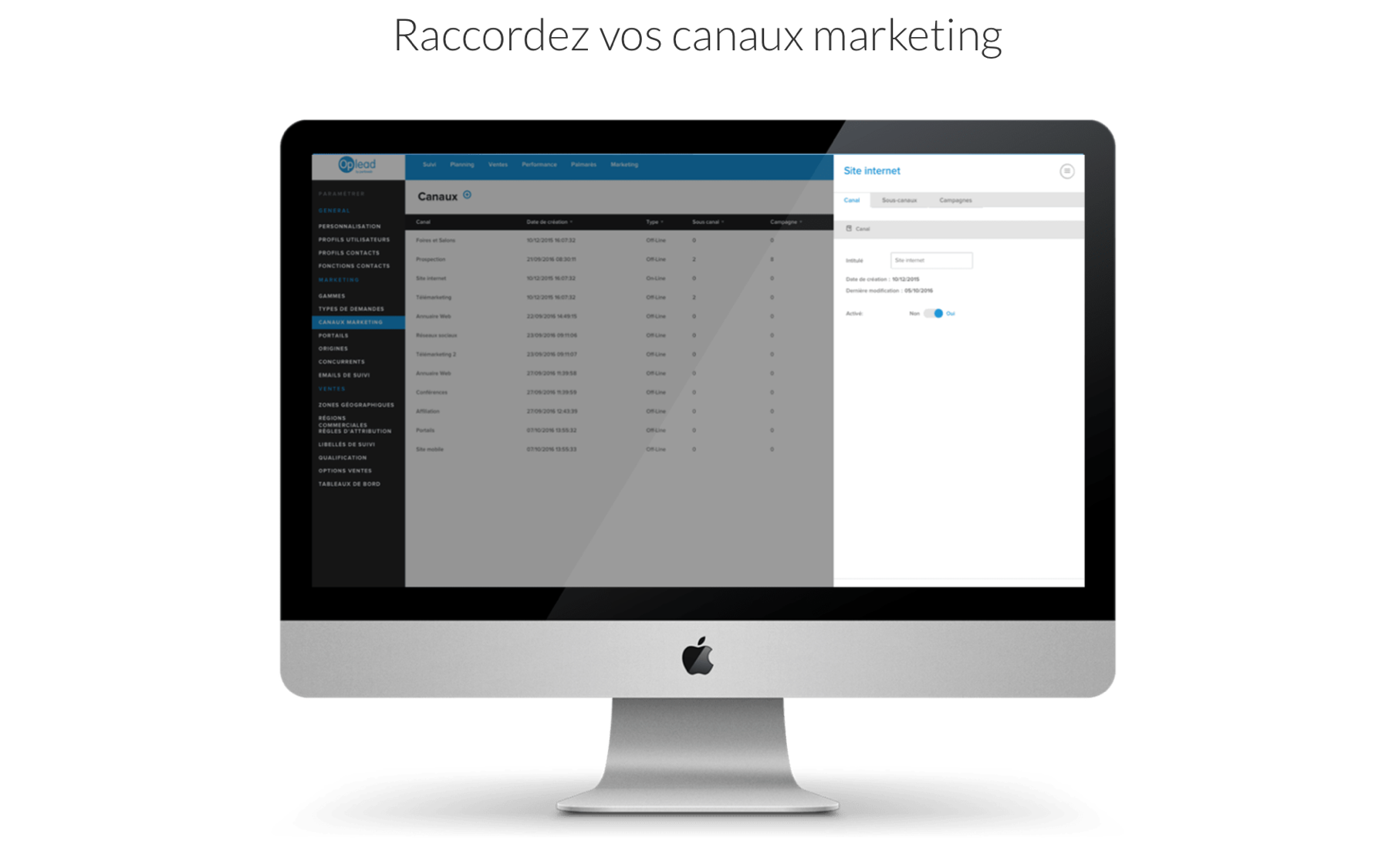 Oplead Lead Management - Managing marketing channels
Oplead Lead Management - Managing marketing channels 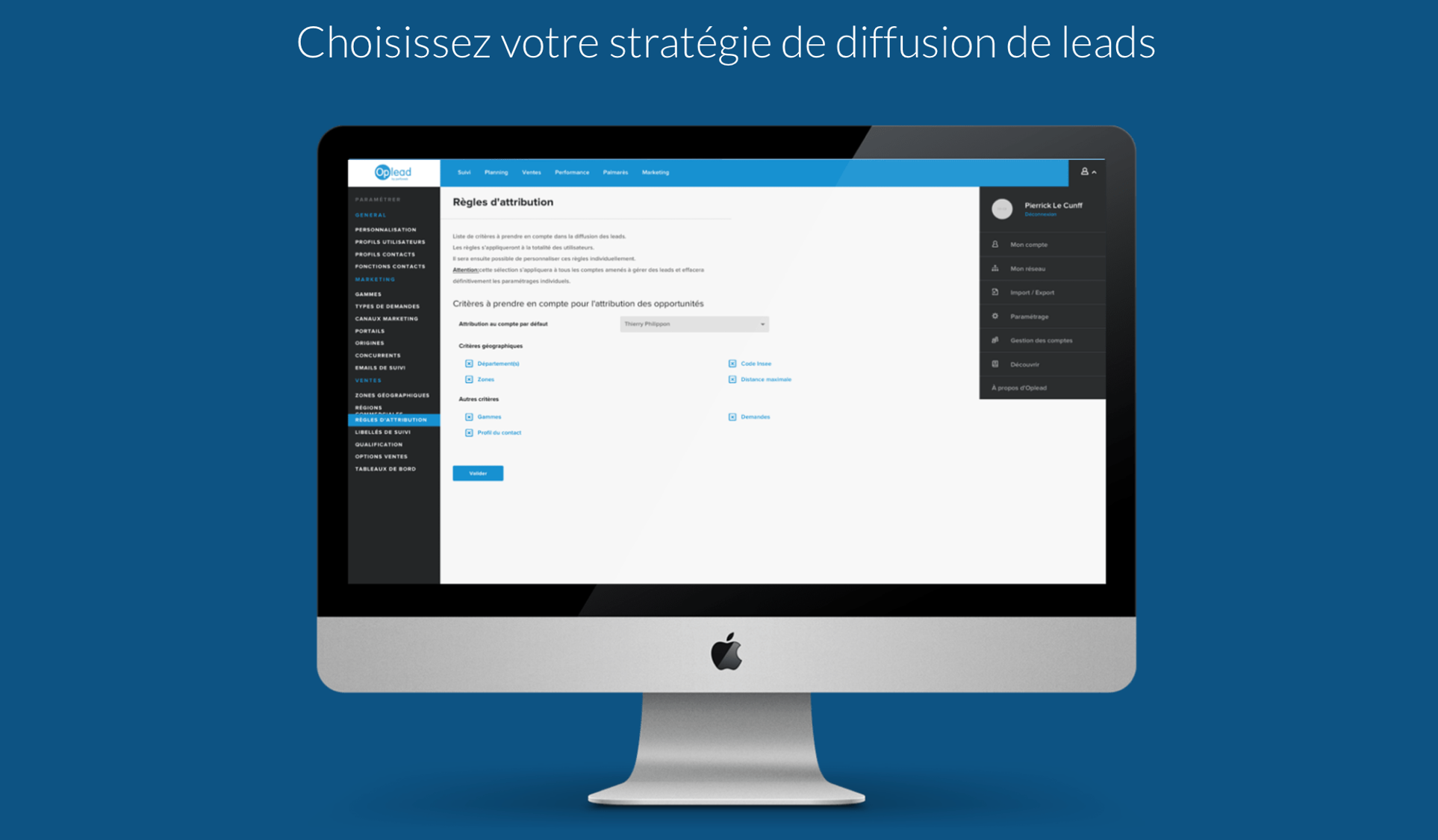 Oplead Lead Management - Broadcasts Lead
Oplead Lead Management - Broadcasts Lead 



Oplead Lead Management: its rates
Standard
Rate
On demand
Clients alternatives to Oplead Lead Management

Streamline sales management with our CRM software. Automate tasks, track leads, and analyze data to increase efficiency and revenue.
See more details See less details
Our CRM software offers a user-friendly interface, customizable dashboards, and real-time reporting. Improve communication with customers and team members, and never miss a follow-up with automated reminders. Gain insights into sales performance and make data-driven decisions to grow your business.
Read our analysis about monday CRMBenefits of monday CRM
Quick Setup and Fast Adoption
Customizable to Fit Any Business Need
Advanced Automation of Repetitive Tasks

Manage your business more efficiently with our powerful Business Management software. Streamline your operations, automate tasks, and increase productivity.
See more details See less details
With our software, you can easily manage your finances, inventory, and customers all in one place. Our user-friendly interface makes it easy to access important data and make informed decisions. Plus, our reporting and analytics tools help you track performance and identify areas for improvement.
Read our analysis about MyBusinessGenie
Streamline your business with powerful management software that simplifies tasks, boosts productivity, and enhances collaboration.
See more details See less details
PYXI's user-friendly interface and customizable features allow you to manage contacts, tasks, projects, and documents all in one place. With real-time updates and automated workflows, you can easily track progress and stay on top of deadlines. Plus, PYXI's secure cloud-based system ensures your data is always safe and easily accessible.
Read our analysis about PYXI Appvizer Community Reviews (0) The reviews left on Appvizer are verified by our team to ensure the authenticity of their submitters.
Write a review No reviews, be the first to submit yours.