ERP SIMAX : Streamline Business Operations with Advanced ERP Solutions

ERP SIMAX: in summary
ERP SIMAX is a cutting-edge enterprise resource planning software designed to optimize business operations for small to medium-sized enterprises. Tailored for business owners and managers seeking efficiency, highlights include real-time data analytics, seamless integration capabilities, and intuitive financial management tools.
What are the main features of ERP SIMAX?
Real-Time Data Analytics
Keep your finger on the pulse of your business with real-time data analytics. Simplify decision-making through comprehensive insights and detailed reporting.
- Detailed dashboards: Provides a graphical representation of key metrics.
- Customizable reports: Tailor-specific reports to fit your business needs.
- Predictive analytics: Identify trends and make calculated business forecasts.
Seamless Integration Capabilities
ERP SIMAX offers seamless integration with both existing software and third-party tools, ensuring that your business systems work together harmoniously.
- APIs for integration: Easily connect ERP SIMAX with other systems using APIs.
- CRM synchronization: Keep your customer relationship management tools in sync.
- Third-party app integration: Expand functionality with a range of app connections.
Intuitive Financial Management
Manage your finances with ease using ERP SIMAX’s comprehensive financial management tools. Stay on top of accounting and streamline your budget operations.
- Automated accounting: Reduce manual entry with built-in accounting automation.
- Expense tracking: Keep a high-level view of your business expenses in real-time.
- Budget management: Efficiently plan and monitor your budgets for better financial control.
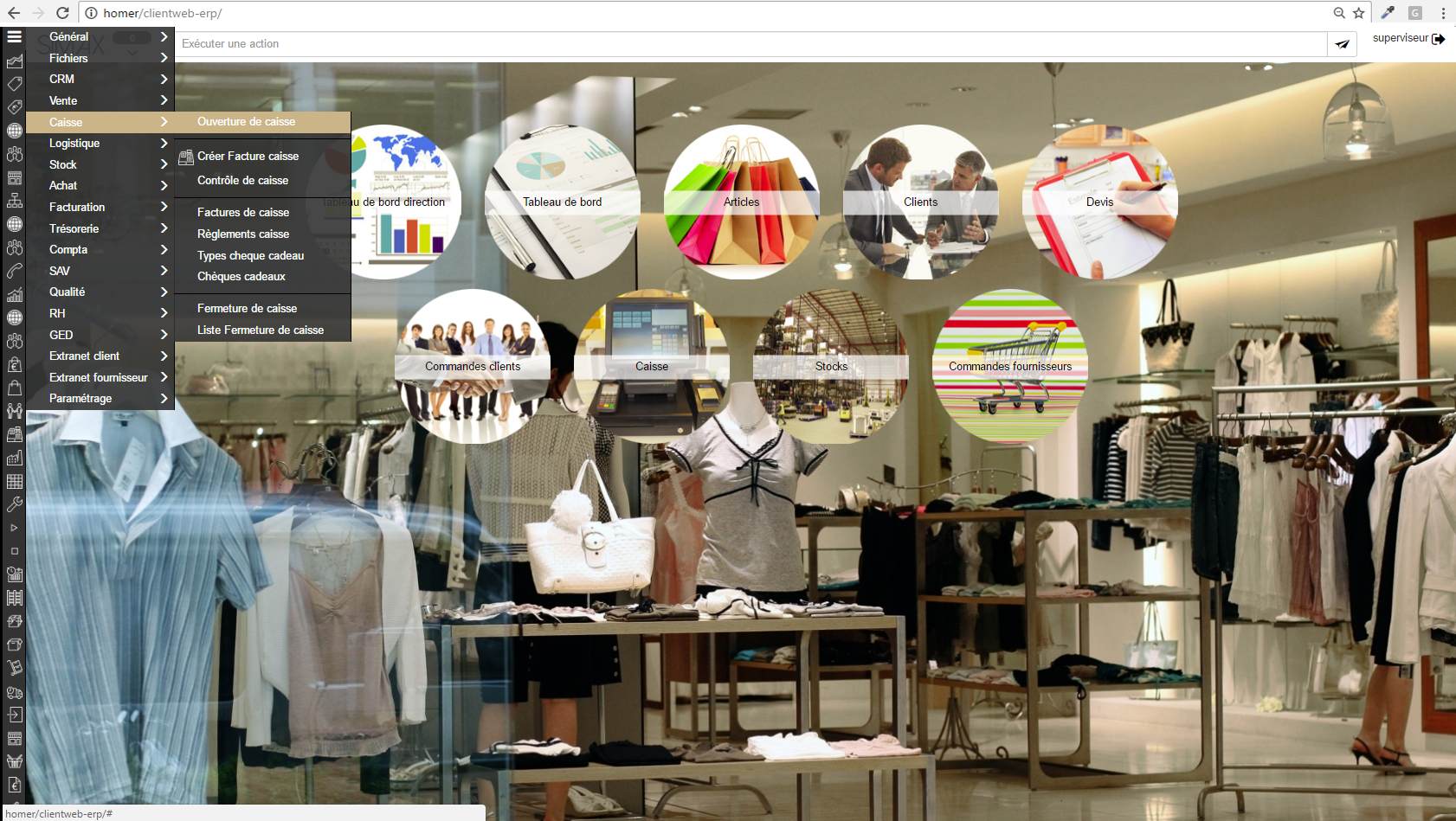 ERP SIMAX - Screenshot 1
ERP SIMAX - Screenshot 1  ERP SIMAX - Screenshot 2
ERP SIMAX - Screenshot 2 

ERP SIMAX: its rates
Standard
Rate
On demand
Clients alternatives to ERP SIMAX

Streamline your business operations with our powerful ERP software. Manage your finances, inventory, and supply chain with ease.
See more details See less details
Our ERP software provides a comprehensive solution for businesses of all sizes. With real-time data analytics, you can make informed decisions and optimize your operations. Our software also offers customizable reporting and integration with other tools to streamline workflows.
Read our analysis about FuriousBenefits of Furious
All-in-one industry solution
Designed by agency and IT services executives
Saves approximately 30% of management time

Comprehensive ERP software for businesses of all sizes. Streamline operations, track inventory, manage finances, and optimize supply chain.
See more details See less details
MyFab ERP software offers a complete solution for businesses to manage all aspects of their operations. With modules for inventory management, financials, and supply chain optimization, businesses can streamline processes and increase efficiency. The software is scalable, making it suitable for small and large businesses alike.
Read our analysis about MyFab
Streamline your operations with a powerful ERP software. Manage your finances, inventory, and sales in one place.
See more details See less details
With this software, you can automate your business processes and gain real-time visibility into your operations. Its intuitive interface and customizable dashboards make it easy to use, while its robust features enable you to optimize your workflows and make data-driven decisions.
Read our analysis about Akuiteo Appvizer Community Reviews (0) The reviews left on Appvizer are verified by our team to ensure the authenticity of their submitters.
Write a review No reviews, be the first to submit yours.
